Understanding the Modern Approach to Building
What is a modular building? It’s a structure built off-site in a factory, using the same materials and codes as traditional construction. The building is created in separate sections, or modules, which are then transported to a location and assembled on a foundation. The result is a building that is virtually indistinguishable from a site-built structure but completed in about half the time.
Key characteristics of modular buildings:
- Method: 60-90% built in a factory, then assembled on-site.
- Codes: Meets or exceeds the same local and state codes as traditional buildings.
- Strength: Often stronger than site-built structures to withstand transport.
- Timeline: 30-50% faster than conventional construction.
- Applications: Offices, classrooms, housing, healthcare, and commercial spaces.
- Types: Permanent Modular Construction (PMC) and Relocatable Buildings (RB).
Many people confuse modular buildings with manufactured or mobile homes, but they are fundamentally different. Modular buildings are real property that appreciate in value, can be financed with traditional loans, and can be built on basements or crawl spaces. The difference isn’t quality—it’s the efficiency of how and where they are built.
Today’s modular buildings serve diverse needs, from multi-story apartment complexes to sophisticated commercial offices. They offer the same architectural appeal as traditional buildings with added advantages in speed, cost, and sustainability.
I’m Sam Zoldock, a commercial real estate investment professional in Alabama. My experience has shown me how modular construction provides the adaptable space that modern businesses need to grow.
What is a Modular Building and How Does It Work?
Modern modular construction is a sophisticated building method that combines factory precision with on-site assembly to create high-quality, permanent structures.
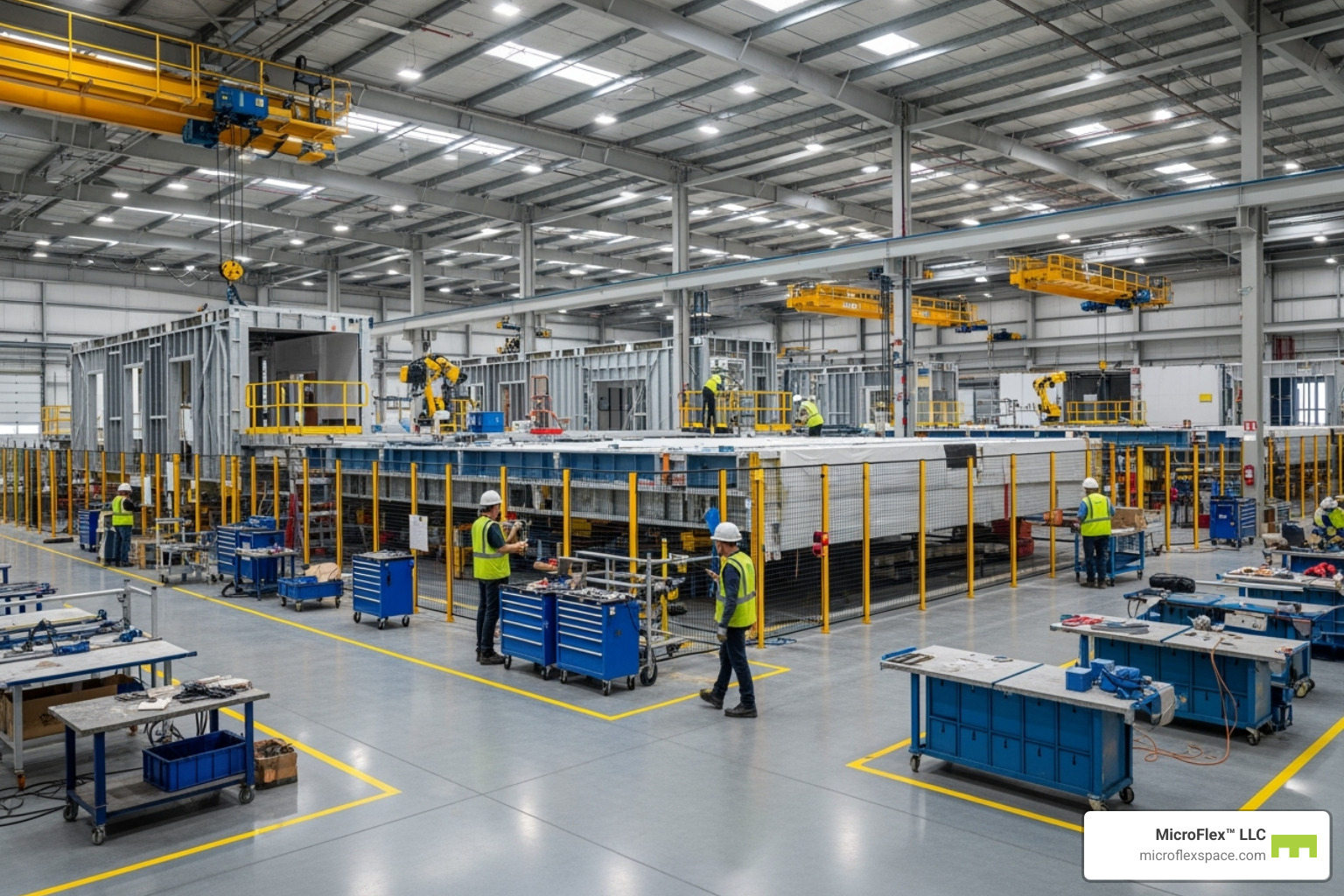
Instead of building everything on a construction site exposed to weather, modular buildings are constructed as three-dimensional sections called modules or volumetric units in specialized, climate-controlled factories. This factory environment allows for lean manufacturing techniques, consistent conditions, and systematic quality checks at every stage, leading to a level of precision that is difficult to achieve outdoors.
Defining the Core Concept: What is a modular building?
A modular building is a structure where 60-90% of the construction happens in a factory. Complete modules are built with framing, insulation, electrical wiring, plumbing, and even interior finishes before they leave the factory.
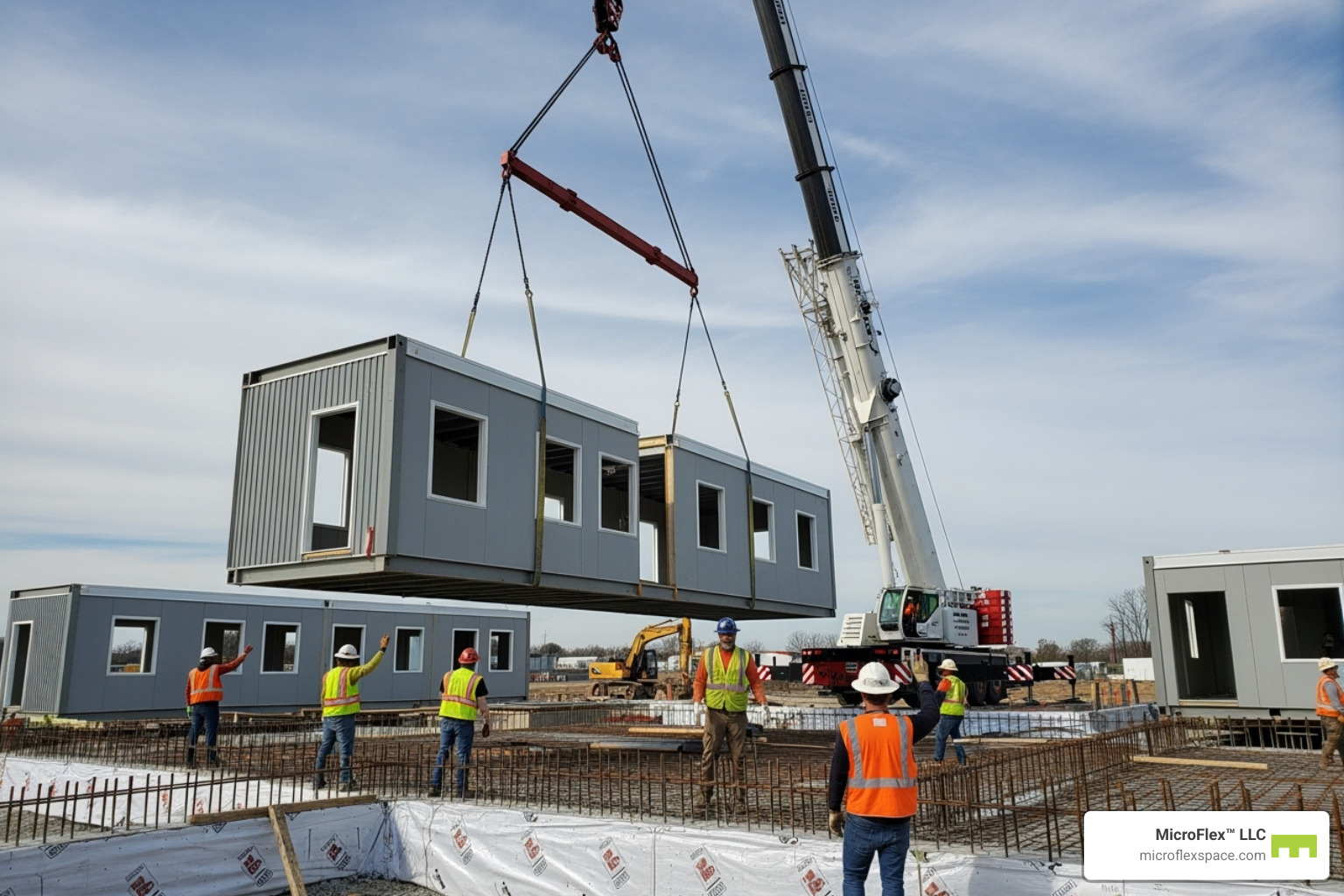
These modules are then transported to the building site, lifted by crane onto a prepared foundation, and connected by skilled crews. Crucially, modular buildings must comply with the same local and state building codes as any site-built structure. In fact, they are often built stronger to withstand the stress of transport and crane lifting.
The efficiency of this approach comes from its parallel construction timeline. While modules are built in the factory, site preparation—such as pouring the foundation and connecting utilities—happens simultaneously. This is a key reason modular projects finish much faster than traditional builds. For more information on industry standards, the Modular Building Institute is an excellent resource.
Permanent vs. Temporary Modular Structures
Modular construction is divided into two main categories: Permanent Modular Construction (PMC) and Relocatable Buildings (RB).
Permanent modular structures are designed for long-term use and installed on permanent foundations. Made from durable materials like wood, steel, or concrete, they are indistinguishable from site-built structures and appreciate in value the same way. They are used for everything from homes and apartments to schools and corporate offices.
Relocatable buildings are designed to be disassembled, transported, and reassembled at new locations. This makes them ideal for temporary needs like construction site offices, interim classrooms, or swing space during renovations. Businesses often use our business rental solutions to tap into this flexibility without long-term commitments. Relocatable buildings are also vital in disaster response, providing rapid deployment of medical clinics, command centers, or temporary housing.
The key difference is not quality but intent: are you building for permanence or for adaptability? Modular construction offers both.
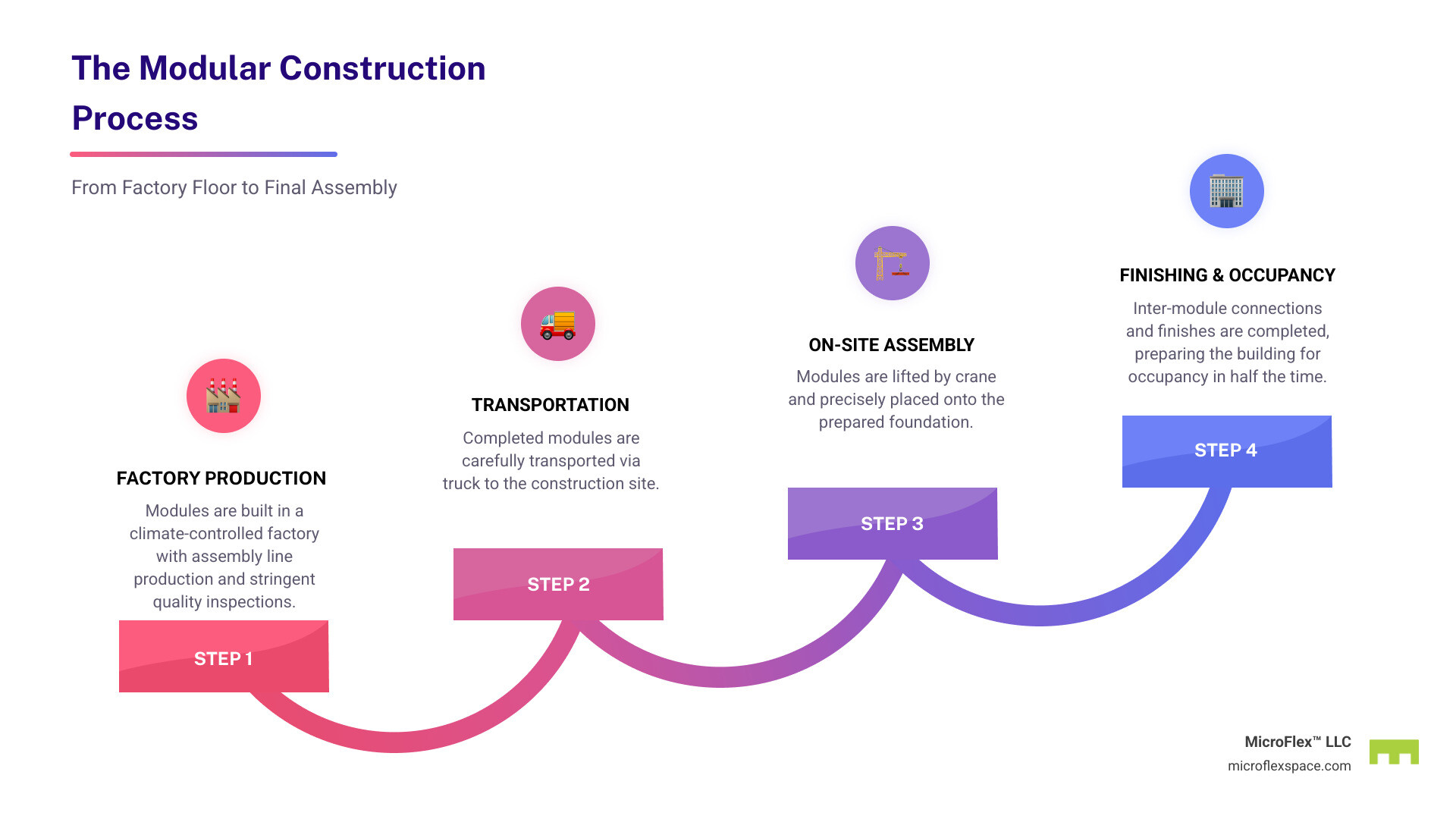
The Modular Construction Process: From Factory to Foundation
The modular construction process is a carefully choreographed sequence of factory production and on-site assembly, resulting in a faster, more predictable timeline than traditional methods.
Step 1: Design and Engineering
This phase is critical, as early decisions impact the entire project. Modern modular design uses Building Information Modeling (BIM) to create detailed 3D digital models, allowing teams to spot issues and make adjustments before construction begins. Architects also use Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA), an approach that optimizes the building for factory production and on-site assembly.
Despite common assumptions, customization is a key feature. Architects can create custom floor plans and exterior designs to meet client needs and local building codes, achieving any architectural style. For a deeper dive, An Introduction for Architects offers valuable insights.
Step 2: Factory Production
Once the design is final, construction moves to a controlled factory environment, protected from weather. Modules are built on assembly lines, where specialized teams work efficiently and with high precision. Quality assurance programs and third-party inspections are integrated throughout the process, catching potential issues early.
A major advantage is MEP integration. All Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing systems are installed and tested in the factory. Interior finishes like flooring, cabinetry, and painting are also completed. By the time modules ship, they are 60-90% complete.
Step 3: Site Preparation and Assembly
Modular construction saves time through parallel construction: while modules are built in the factory, the site crew prepares the foundation and utility connections. This eliminates the linear delays of traditional building.
Once modules are ready, they are transported to the site. On-site assembly is often the most dramatic phase, as a crane lifts and places each module onto the foundation. A multi-story building can take shape in just a few days.
Crews then make inter-module connections, joining the sections and linking utilities. Exterior finishing and roofing complete the building envelope, a process known as “weathering-in.” After final inspections, the building is ready for occupancy far sooner than a traditional build.
Modular vs. Traditional vs. Manufactured: Clearing the Confusion
Understanding the differences between modular buildings, traditional site-built construction, and manufactured homes is key. People often lump all factory-built structures together, but they differ significantly in codes, financing, and long-term value.
- Modular Buildings: Built in sections in a factory to the same state and local codes as site-built homes. They are transported to the site, placed on a permanent foundation, and are considered real property that appreciates in value.
- Site-Built Construction: The traditional method where a structure is built entirely on its final location.
- Manufactured Homes (or Mobile Homes): Built on a non-removable steel chassis to a single federal HUD code. They are considered personal property in many states and often require specialized financing.
This distinction is crucial for investment. Modular buildings are financed with traditional mortgages and hold their value like site-built structures, making them a solid choice for business properties.
Key Differences from Site-Built Construction
While the end product is equivalent, the process of modular construction offers distinct advantages over traditional building.
- Timeline: Modular construction is 30% to 50% faster due to parallel work in the factory and on-site.
- Weather Delays: Factory production is immune to weather, keeping projects on schedule and on budget.
- Material Waste: Lean manufacturing in factories can reduce material waste by up to 90% compared to messy job sites.
- Site Disruption: With most work done off-site, there is minimal noise, traffic, and disruption to the surrounding community.
- Quality Control: A controlled factory environment with consistent inspections often results in superior craftsmanship and a tighter building envelope.
How to Identify a Modular Building
Modern modular buildings are visually indistinguishable from their site-built counterparts. However, if you’re curious, there are a few clues.
Look for small metal data plates or tags in inconspicuous places like inside a kitchen cabinet, a closet, or near the electrical panel. These tags provide manufacturer and code compliance information.
The biggest clue is the foundation. A modular building will sit on a permanent foundation (slab, crawl space, or basement) just like a site-built home. If you see a steel frame or chassis underneath, it is a manufactured home.
The key takeaway is that modular buildings are not a lesser form of construction. Our Pre-Fab Offices are permanent, professional structures designed for serious business use.
The Core Advantages: Why Businesses are Choosing Modular
Why are so many businesses, including those seeking Dynamic Workplace Solutions, turning to modular construction? The advantages directly address the common pain points of traditional building methods.
Speed and Cost-Efficiency
In business, time is money. Modular buildings can be completed 30-50% faster than traditional projects. This speed comes from parallel construction—building modules in a factory while the site is being prepared. Weather delays are virtually eliminated, keeping the project on a predictable schedule.
Cost savings are also significant, typically 10-25% compared to conventional construction. This is due to efficient factory labor, up to 90% less material waste, and reduced financing costs. Most importantly, a faster completion date means an earlier return on investment, as your building can be occupied and generating revenue months sooner.
Quality, Durability, and Safety
Faster does not mean lower quality. In fact, modular buildings are often stronger than site-built structures. Modules must be engineered to withstand transportation and crane lifting, requiring extra reinforcement. This inherent strength means some modular buildings can withstand hurricane-strength winds up to 175 mph.
Factory precision ensures exact measurements and consistent craftsmanship in a controlled environment, free from outdoor variables. Quality control is performed at every stage, and third-party inspectors verify compliance with all local and state building codes, as detailed in this Primer on Off-Site Construction Codes and Compliance. Furthermore, moving construction into a factory reduces on-site accidents by an estimated 80%.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Modular construction is one of the greenest building practices available. The factory process generates up to 90% less material waste through precise cutting and recycling programs. Reduced site disturbance means less noise, dust, and traffic, minimizing the impact on the surrounding community.
Factory assembly also creates a tighter building envelope, which improves insulation and leads to lower heating and cooling costs over the building’s lifetime. This contributes to better energy efficiency and improved indoor air quality, creating healthier spaces for occupants.
Design, Customization, and Practical Considerations
One of the biggest myths about modular construction is that it produces boring, cookie-cutter boxes. The reality is that modern modular offers remarkable design flexibility to create unique and functional spaces for any business need.
Can Modular Buildings Be Customized?
Absolutely. Today’s modular buildings can be designed in virtually any architectural style, from traditional to contemporary. You can customize nearly every aspect, including:
- Facades and exterior finishes (brick, stucco, metal, etc.)
- Roofing styles and materials
- Custom floor plans for open-concept or private office layouts
- Window configurations to maximize natural light
- Multi-story capabilities for offices, hotels, or apartments
- Integration with existing buildings for seamless expansions
- Smart technology for energy management, security, and automation
Whether you need a modular office space or a Creative Workspace for Rent, the design possibilities are vast. The only key difference is that design decisions must be finalized earlier in the process, before factory production begins. This upfront planning leads to a smoother, more predictable project with fewer surprises.
Financing, Insurance, and Permitting
For permanent modular structures, these processes are nearly identical to those for traditional construction.
- Financing: Banks and lenders treat permanent modular buildings the same as site-built properties. You can secure conventional construction loans and mortgages, and the buildings appreciate in value similarly.
- Insurance: You will obtain standard property insurance with comparable rates to a site-built structure.
- Permitting: The project must go through the same local permitting process to ensure compliance with zoning and building codes. An experienced modular provider can help steer this process smoothly.
Choosing modular doesn’t mean sacrificing design, financing, or quality. It means choosing a smarter, faster way to build.
The Evolution and Future of Modular Buildings
The concept of prefabrication is not new; it’s a time-tested approach refined over generations. Its roots stretch back to the 1830s, when a prefabricated home was shipped from England to Australia. The method gained traction during the California Gold Rush for rapid housing and was used extensively to build military facilities during World War Two and address post-war housing shortages.
Today, the future of modular construction is being shaped by technology and sustainability. Key trends include:
- Mass timber construction: Using materials like Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) to create strong, sustainable, and taller modular structures.
- Digital fabrication: Integrating 3D printing and advanced CAD systems for unprecedented precision and efficiency in the factory.
- Smart technology integration: Building intelligent environments with built-in IoT devices to manage energy, monitor air quality, and optimize building performance.
- High-rise modular construction: Applying modular techniques to build towers and large-scale urban developments, proving the method’s scalability.
The applications are expanding to extreme environments like the Halley VI Research Station in Antarctica and critical infrastructure like healthcare facilities. This evolution aligns with what modern businesses need: spaces that are quick to deploy, adaptable, and built to the highest standards. The core idea has always been to build better and faster—and today’s technology is making that more possible than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions about Modular Construction
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions about what is a modular building.
How long do modular buildings last?
Permanent modular buildings are designed for longevity. Built with durable materials like steel and concrete to the same codes as traditional construction, they are expected to last 50 years or more, just like their site-built counterparts. They appreciate in value and are a long-term asset.
Relocatable buildings, while also durable, are designed for flexibility. Their lifespan depends on use and maintenance, but they can serve temporary needs effectively for many years.
Are modular buildings cheaper than traditional construction?
Yes, modular construction is typically more cost-effective, with most projects seeing savings of 10-25%. These savings come from several sources: reduced labor time in an efficient factory setting, minimized material waste (up to 90% less), and a shorter construction schedule that lowers financing costs and allows for a faster return on investment.
What are the main disadvantages of modular construction?
Like any method, modular has its challenges. The three main considerations are:
- Transportation logistics: Modules are large and require careful planning for transport from the factory to the site, including route selection and permits.
- Site access: The construction site must have enough space for large trucks and the crane needed to place the modules.
- Early design finalization: Because production happens quickly, design decisions must be locked in earlier than with traditional construction, offering less flexibility for mid-project changes.
Working with an experienced modular builder helps manage these challenges effectively.
Conclusion: Building the Future, Flexibly
We’ve seen that what is a modular building is a story of innovation. Modular construction is often a better choice than traditional methods, offering a powerful combination of speed, cost-effectiveness, superior quality, and sustainability.
Buildings completed in half the time, built stronger, and with up to 90% less waste are not just a novelty—they represent smart construction for the modern world. These structures meet the same codes, secure the same financing, and appreciate in value just like traditional buildings.
This adaptability is at the heart of what we do at MicroFlex™ LLC. We understand that modern businesses need flexible spaces that can evolve. Our multi-use commercial property solutions in Birmingham, Alabama, accept this modular mindset, providing spaces that adapt to your changing needs.
Whether you’re considering a permanent modular building or need flexible commercial space to grow, the principles of efficiency and quality are key. If your business is ready to expand, explore our Business Expansion Space options. We’re here to help you find a solution that works for today and tomorrow.